Stakeholder engagement and materiality analysis
Listening to stakeholders is a crucial step in defining strategic decisions as well as in the Group’s daily operations. Banco BPM’s organizational model includes specialized corporate functions responsible for overseeing key stakeholders.
Our stakeholders and the communication channels
Our strategy and the definition of the materiality topics stem from listening to stakeholders.
Materiality analysis
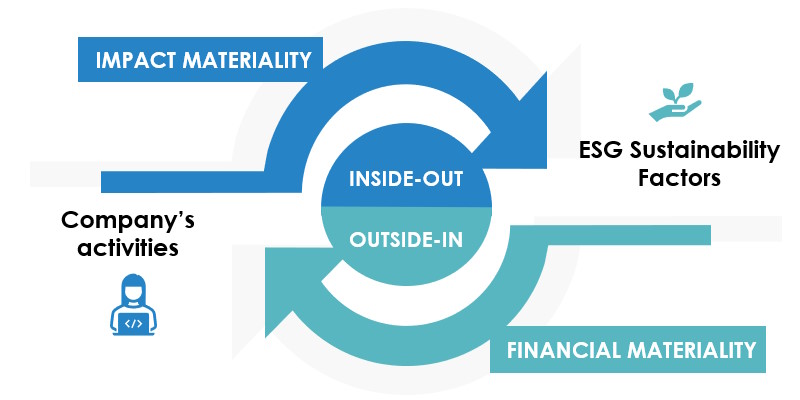
For its 2024 Sustainability Reporting, Banco BPM has adopted a new approach based on the principle of double materiality, in compliance with the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD).
The process was divided into four main phases:
1. Context analysis, with a mapping of activities, stakeholder relationships, and key areas of impact.
2. Identification of impacts, risks, and opportunities (IROs) related to ESG issues, both within the Group’s activities and its value chain.
3. Assessment using qualitative and quantitative criteria, with scoring.
4. Final validation with the involvement of external stakeholders, independent experts, and internal governance bodies.
This methodology allows for a broader identification of the topics to be reported, going beyond the traditional approach and ensuring a complete representation of the Group’s responsibilities and exposures to sustainability issues.